GP Dentist Prometric DHA MOH EMREE DHCC HAAD SDLE QCHP OMSB answers to questions on Social Media Pages
On 27-05-2020 | Read time about 8 Minutes
This page brings together all answers of GP Dentist questions posted on our Social Media Pages for Prometric DHA exam for Dubai - MOH exam for Sharjah and other emirates - EMREE exam questions- DHCC exam for Dubai Health Care City- DOH (HAAD) exam for Abu Dhabi and Al Ain - SDLE exam for Saudi - QCHP exam for Qatar and OMSB exam for Oman
Find the Prometric Questions to answers posted below
To solve past questions, with correct answers and learn clincial rationales developed by our team using all the features that will aid you in productive, cluter free learning, visit our Solve Questions Page here
The correct answer to Question Posted on 26th August is Option C.
The correct answer to Question Posted on 22nd July is Option C.
The correct answer to Question Posted on 17th July is Option C.
The correct answer to Question Posted on 30th May is Option B.
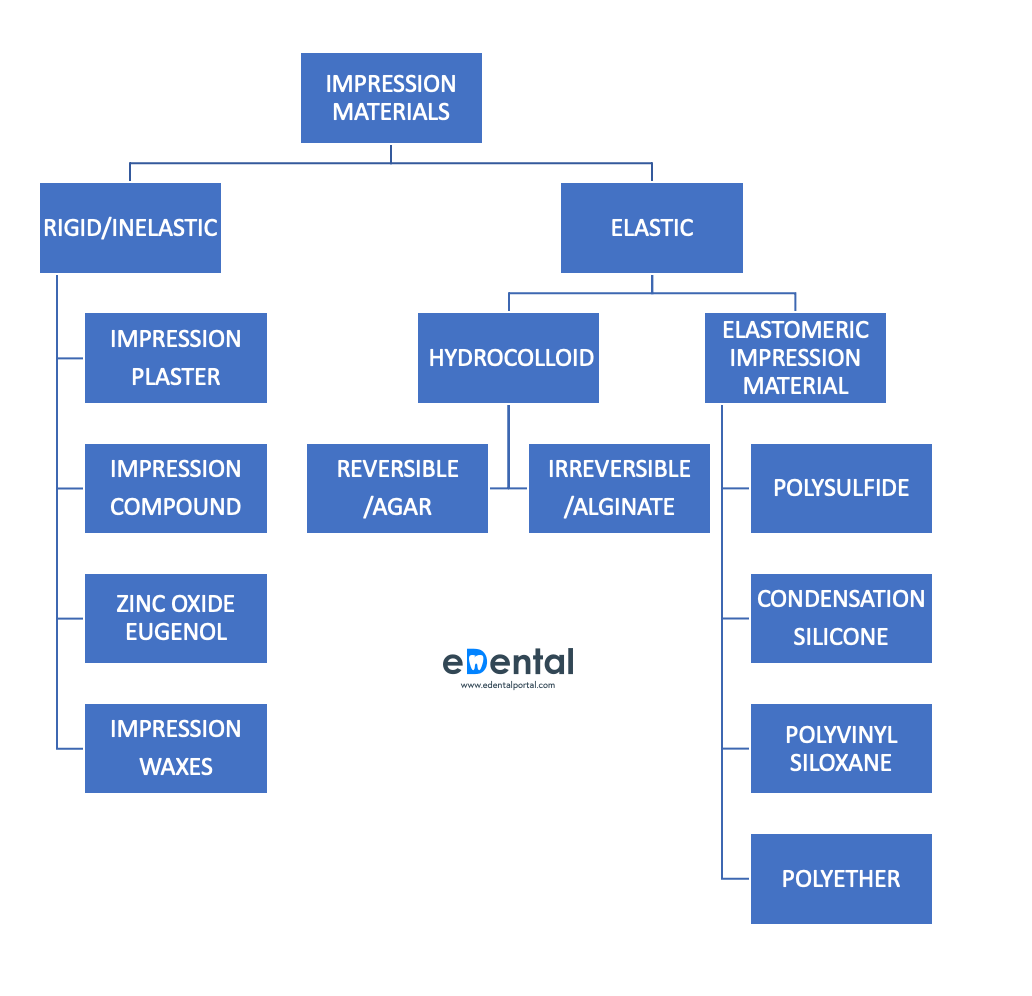
Similar questions can be found in the Explanations to questions under Study > Diagnostics and Basic Sciences > Others
The correct answer to Question Posted on 13th May is Option B.
This can be found in the Explanations to questions under Study > Endodontics > Pulpal diagnosis and also under Study > Pediatric Dentistry > Others
The correct answer to Question Posted on Instagram on 9th May 2023 is Option A
If there is a pin point exposure, then attempt a direct pulp cap with calcium hydroxide and cover with an acid-etch retained composite restoration.
If there is a large exposure, then the tooth will need some form of pulp treatment: Cvek pulpotomy/partial pulpotomy or full pulpotomy to try to maintain vitality of the pulp tissue.
Option C is done with primary teeth while the question addresses a permanent tooth.
Option D: If the tooth is non vital, then a pulpectomy is completed
Similar questions can be found in the Explanations to questions under Study > Pediatric Dentistry > Pediatric Pulp Therapy on eDental Portal.
The correct answer to Question Posted on Instagram on 16th May 2023 is Option D
Option A is done if a tooth is non-restorable, or has furcation involvement or has internal or external root resorption, it should be extracted.
Option B is carried out on symptom-free tooth; with minimal caries in an area that, if caries were removed would result in a pulp exposure.
Option C is done with Vital primary tooth with carious or accidental exposure, with clinical signs of a normal pulp canal. If the tooth in the given question was vital, then it would have responded to pulp testing.
Option D: Pulpectomy is carried out on Necrotic (In the given question the tooth does not respond to pulp test and is carious) or chronically inflamed. If the tooth had pain, pulpectomy would offer pain relief on teeth with irreversible pulpitis until nonsurgical endodontic treatment can be performed.
Similar questions can be found in the Explanations to questions under Study > Pediatric Dentistry > Pediatric Pulp Therapy on eDental Portal.
The correct answer to Question Posted on Instagram on 23rd May 2023 is Option B
“Primary Failure of Eruption,” is a rare disease with incomplete tooth eruption despite the presence of a clear eruption pathway and key manifestations involving partial or complete noneruption of initially non-ankylosed teeth due to a disturbed eruption mechanism. A prominence or bulge is evident where the impacted tooth’s crown lay.
The ideal time to surgically intervene to expose an impacted tooth is when the root of the impacted tooth is almost completely formed and the apex is not yet closed.
The affected teeth is not ankylosed, but tend to become ankylosed when applying an orthodontic traction force.
Similar questions can be found in the Explanations to questions under Study > Pediatric Dentistry > Developmental Disturbances
The correct answer to Question Posted on 8th June 2023 is Option B.
The correct answer to Question Posted on 8th May is Option A.
During the symptomatic phase of infection, detection of antibodies to HBeAg and HBsAg is obscured because the antibody is complexed with antigen in the serum. Easier ways to remember above information will be found under Study > Diagnostic and Basic Sciences > Infection Control
Latest Posts

FREE PROMETRIC PRACTICE TESTS
Try out the most relevant Prometric mock test questions for Dental exams here.
ENROLL NOW